The power of music, as we already know, is astounding, and its possible applications in so many different contexts makes it more and more fascinating.
Besides the healing qualities that music itself has, we can find many, let’s say, technical application that allow it to work with science.
Here I would like to focus on its application in the medical field, in particular in physiotherapy (rehabilitation).
But how and why could it be useful?
Well, classical physiotherapy is sometimes repetitive (boring), not cheap at all (due to one-to-one treatments) and can’t be really monitored at home.
So… could we solve these problems using music? Well, the answer is yes.
A project that particularly interests me in this field is PhysioSonic, developed in IEM Graz.
Using a tracking system, the human body is detected and its data is used to synthesize and / or transform audio files. This provides the patient with auditory feedback, which allows him to understand whether the exercise was performed correctly or not.
Here is their statement about the project:
“In PhysioSonic, we focus on the following principles:
- The tracking is done without a disturbance of the subject, as markers are fixed to an overall suit (and the subject does not, e.g., have to hold a device).
- In collaboration with a sport scientist, positive (target) and negative (usually evasive) movement patterns are defined. Their range of motion is adapted individually to the subject. Also, a whole training sequence can be pre-defined.
- The additional auditory feedback changes the perception including the proprioception of the subject, and the move- ments are performed more consciously. Eyes-free condi- tion for both the subject and an eventual observer (trainer) free the sight as an additional modality. In addition to the target movement, pre-defined evasive movements are made aware.
- We sonify simple and intuitive attributes of the body move- ment (e.g., absolute height, velocity). Thus, the subject eas- ily understands the connection between them and the sound. This understanding is further enhanced by using simple me- taphors: e.g., a spinning-wheel-metaphor keeps the subject moving and thus ’pushing’ the sound; if the subject does not accumulate enough ’energy’, the looping sound of a disk- getting-stuck metaphor is used.
- The sounds are adapted to each subject. Music and spoken text that are used as input sounds can be chosen and thus en- hance the listening pleasure. Also, the input sounds change over time and have a narrative structure, where the repeti- tion of a movement leads to a different sound, thus avoiding fatigue or annoyance. (Still, the sonification design is well-defined, and the quality of the sound parameters changes according to the mapping.) “
The tracking system used is the VICON tracking system that allows a spatial resolution in the millimeter range and a temporal resolution and reaction time less than 10 ms. This means that it detects movements really precisely.
The data is then processed in the VICON system and used in SuperCollider (platform for audio synthesis and algorithmic composition) to synthesize and process sounds. The system allows a very detailed continuous temporal and spatial control of the sound produced in real time.
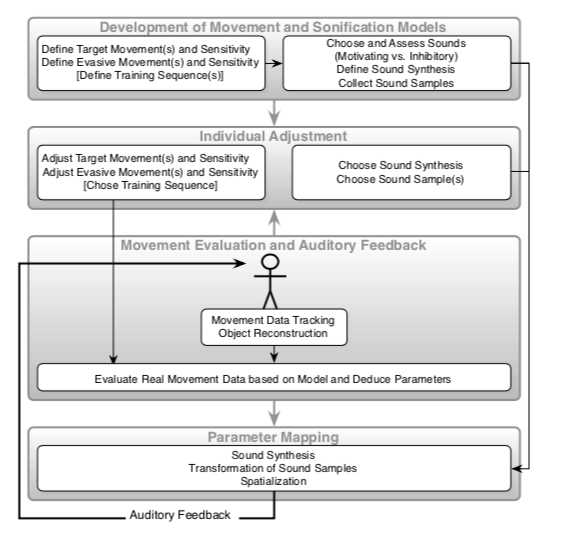
Some videos can be found at https://iem.at/Members/vogt/physiosonic
Currently, this system is set up at the hospital Theresienhof in Frohn- leiten, Austria.
Reference:
[1] K. Vogt, D.Pirro ́, I. Kobenz, R. Höldrich, G. Eckel – Physiosonic – Movement sonification as auditory feedback. 2009.