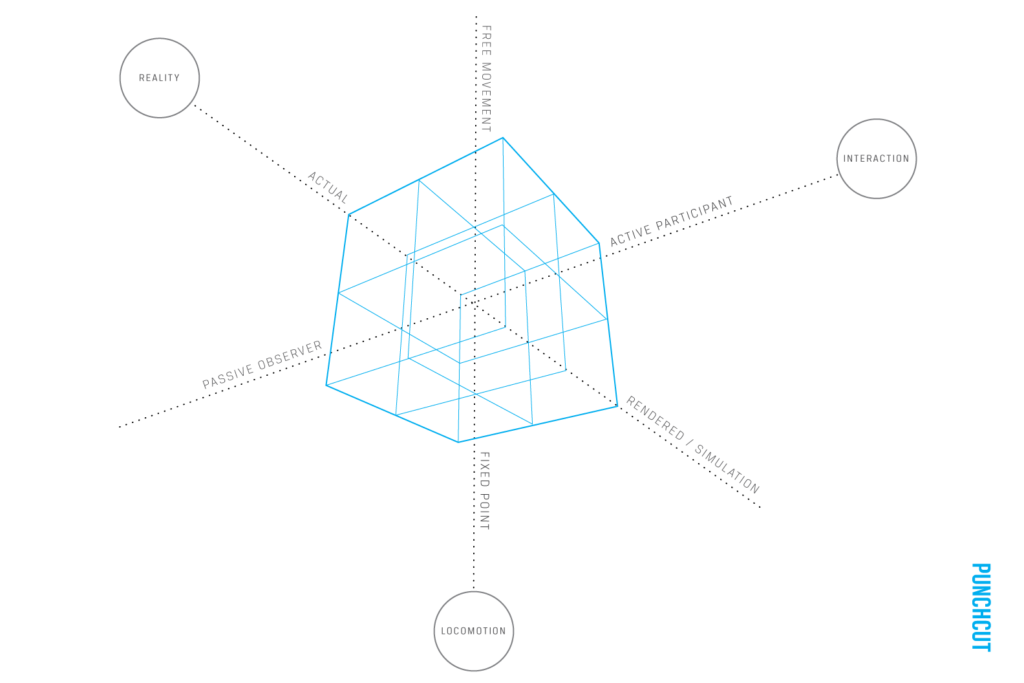
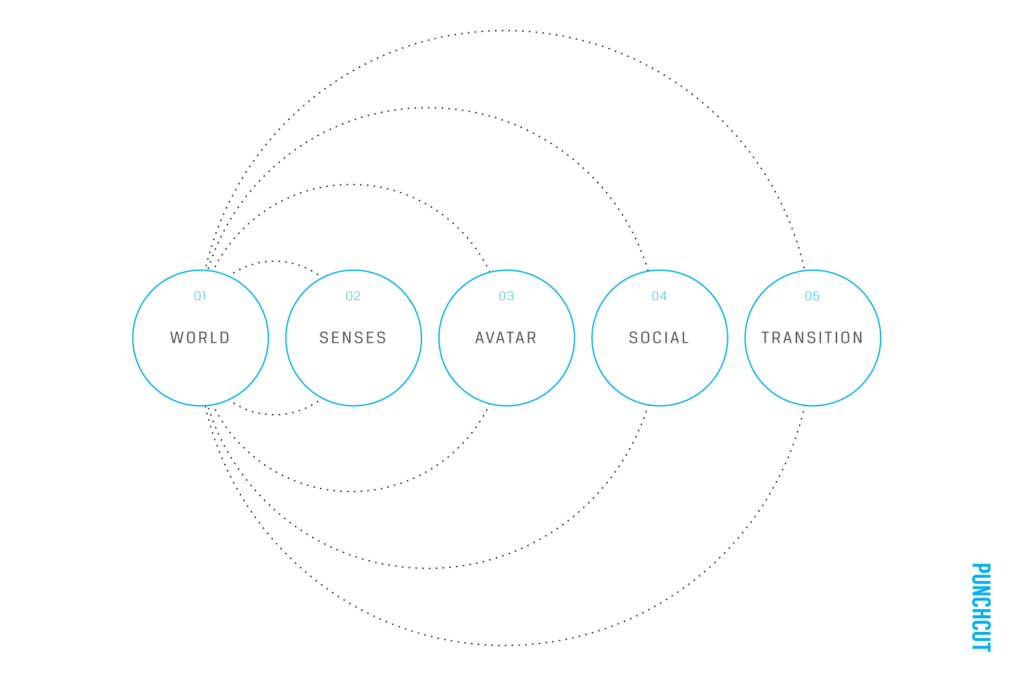
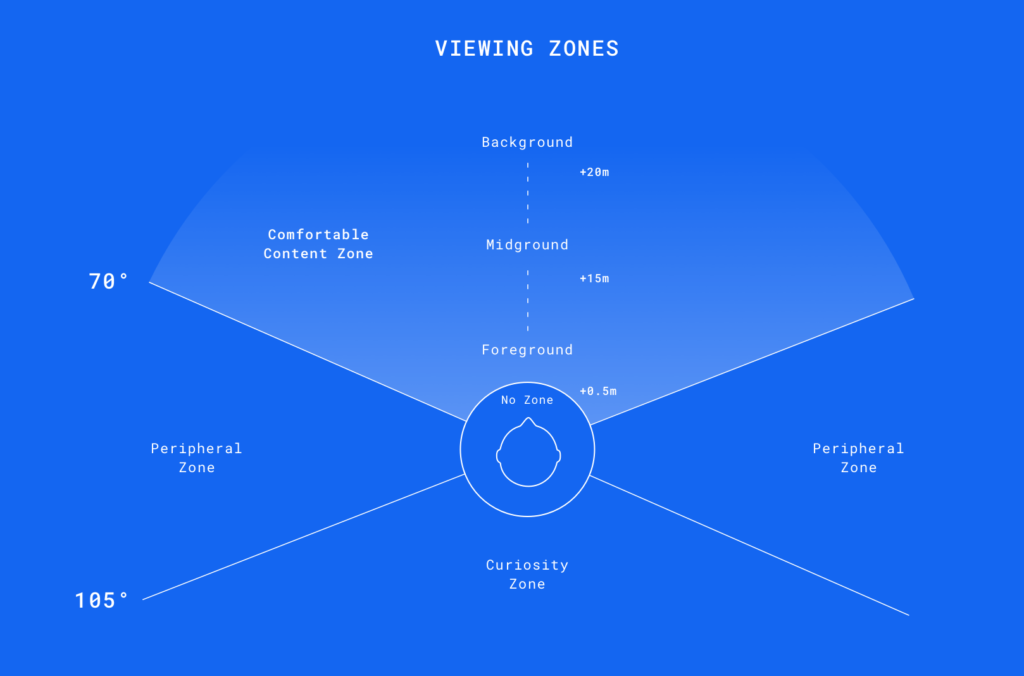
Customer Experience app with focus on AR-enhanced marketing opportunities and creation of a new unique selling point for the company Gehmacher based in Salzburg, by Janina Schindler and Carina Steindl.
About the company.
Our environment influences us. No matter if material or immaterial. We want to inspire you to surround yourself with beautiful things and thus create quality of life. With furniture and accessories in your home, the clothes you wear and beauty in your encounters. We believe that the beauty affects our life in a positive way.
There is hardly any other city that fits “living in beauty” as well as Salzburg. Beauty and excellence can be found in the impressive architecture, the style of the Salzburgers and in nature in the form of the mighty mountains and the Salzach. The Gehmacher house on the Alter Markt is located right in the heart of the city and has been owned by the Gehmacher family for over 100 years.
There are now three main areas at Gehmacher: HOME, CLOTHING and a Café. But there is a common philosophy behind this: to create quality of life through beauty. To create places where you can recharge your batteries, enjoy and experience joie de vivre. To create an atmosphere that inspires with the right interior and to underline the inner beauty with the right outfits. We are constantly in the process of developing our range and finding new things. Timeless and yet in tune with the times.
Gehmacher – a family company characterized by tradition and constant change. Once a specialist shop for bedding and curtains, which, after remaining undamaged in World War II, has developed into the address for furniture and lifestyle products. Today there are eight stores: HOME, CLOTHING, LIFESTYLE, RETTL X GEHMACHER, HIGH FASHION, OUTDOOR & CAFÉ, CLASSICS and N°8 reaching from Alter Markt to Waagplatz.
The persistent longing for beauty, atmosphere and experience has always driven us. Gehmacher changes with every generation. However, always with the aim of carrying on the legacy and giving it an individual touch. Gehmacher – a family company that is deeply anchored in its own values and has its heart and focus on the future.

Briefing
In order to turn the Gehmacher customers into fans and family and thus to bind them even more to the company Gehmacher, a Gehmacher customer app is going to be developed that will provide the customer with information, inspiration and other benefits. The app should also support the Gehmacher team with different features and create another USP for the company Gehmacher.
Concept Requirements
- Web-based App
- Marketing Tool
- Easy to use and aesthetically appealing
- Privacy
- Support for the team and enrichment for the customers
- UX Testing
- Working Prototype ready for implementation
Features
- VIP (Stammkunden) speacial Discounts etc.; QR or NFC (according to individual sales)
- Personalized Newsletter
- „Personalized“ Posts – Feed (bsp. LinkedIn, etc.) Inspiration for the 3 areas (HOME, CLOTHING, CAFÉ)
- Scheduling with salesperson (Private Shopping/ Interior Design Appointments)
- Private event invitations via App
- Stores and Contact persons are introduced (favorite advisor/salesperson)
- Map cooperation opportunities (Products, Shootings, SM, etc.)
- Link to SM Accounts & Website (Blog etc.)
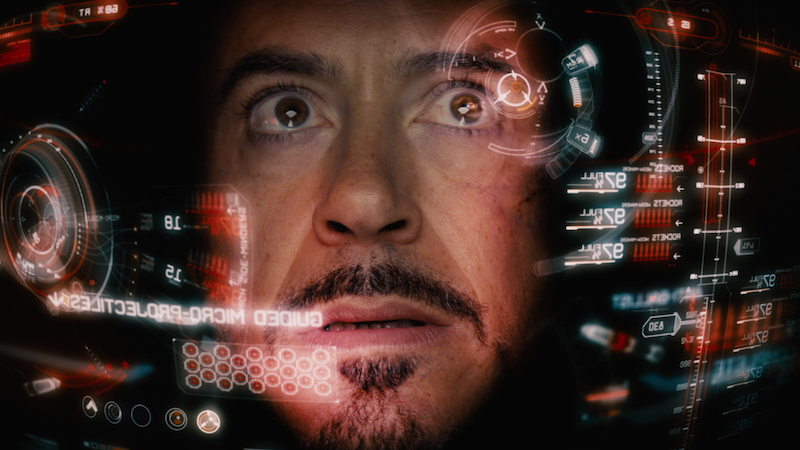
- Possibility for interactive outdoor advertising (AR, etc.)
Team
Janina and me are starting with the project in the third (this) semester.
- Janina Schindler B.A. & Carina Steindl B.Sc. (Research, Conception, UI/UX, Prototype, Basic Programming, Testing)
- Project management & communication – Carina Steindl B.Sc.
- Client: Otto Gehmacher G.m.b.H & CoKG – Julia Gehmacher B.A. (CEO), Franziska Lüdtke (Marketingteam), etc.
We split up the research into different topics and assigned them like follows (changes can happen during the research):
Research topics for the WS21/22:
- Introduction to the Topic – Carina Steindl
- AR in the Marketing field – Janina Schindler
- General Market Research – Carina Steindl
- Web or native App – Janina Schindler
- CX & UX for apps in retail – Carina Steindl
- USP enhanced CX – Janina Schindler
- Personas, User Research – Carina Steindl
- User/Customer journey, scenarios – Janina Schindler
- Concepts for backend/team support – Carina Steindl
- User Interface of comparable App – Janina Schindler
- Image Tracking in AR – Carina Steindl
- General CX in retail – Janina Schindler
- User/Customer Journey on site in the store – Carina Steindl
- AR critical consideration – Janina Schindler
Milestones WS21/22:
- Topic Assignments and Planning – 24.10.2021
- First discussion of research Results – 29.11.2021
- Presentation and workshop at the company – 06.12.2021
- Research & first ideation presentation online – 20.12.2021
- evtl. additional presentation & feedback round at the company – 21.01.2022
- Concept presentation – 31.01.22/KW6 2022
Additionally to the milestones we have a weekly jour fixe.