Reality – Virtuality Continuum
The Reality-Virtuality Continuum is very well-known and was already defined in 1994 by Paul Milgram. His paper “A Taxonomy of Mixed Reality Visual Displays” focused on Mixed Reality (MR) visual displays. He described MR as a
“subset of Virtual Reality (VR) related technologies that involve the merging of real and virtual worlds somewhere along the ‘virtuality continuum’ which connects completely real environments to completely virtual ones.”
Paul Milgram, 1994
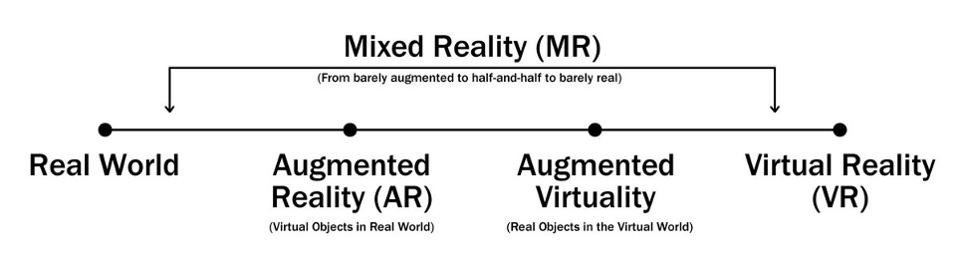
His virtuality continuum explains the different steps in the transition from real environments on one end to completely virtual and computer-generated environments on the other end. Although these terms have already been officially defined, some of them are still not used correctly.
Extended Reality (XR)
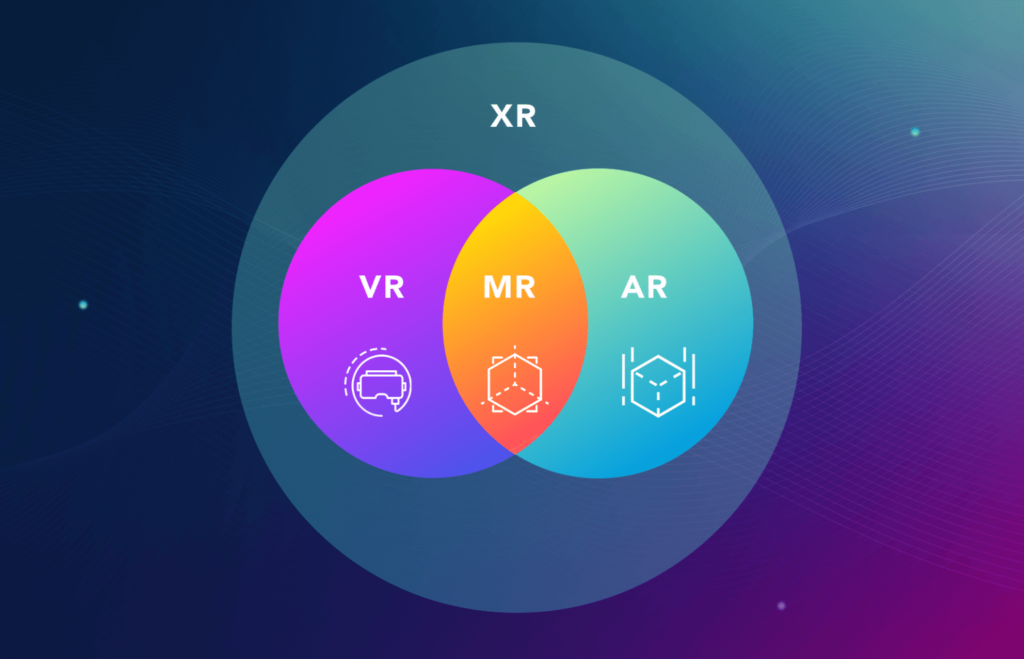
The term Extended Reality (XR) is relatively new. Sometimes it is also described as Cross Reality or X-Reality. It is an umbrella term for all combinations of real and virtual environments that are currently existing. XR will also include all immersive technologies that get developed in the future. Extended Reality technologies are already in use in several industries. Because they are also continuously getting cheaper and better they will be used even more in the future. The most popular XR technologies at the moment are Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR).
Mixed Reality (MR)
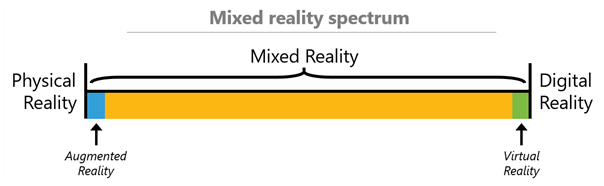
Mixed Reality is often used interchangeably with Augmented Reality (AR) but that’s wrong. It is an umbrella term for everything between the real world and the virtual world – including Augmented and Virtual Reality. MR blends the real world with the virtual world and creates complex environments. Because of these similarities, it is also hard to distinguish AR, VR and MR devices and applications. The most popular Mixed Reality device is the Microsoft HoloLens.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality describes a real-world with an overlay of computer-generated information. Because there is no immersion into a virtual world, the real environment is still the center of information. The real world is just expanded with a projection of animations, infographics, videos, images, 3D objects, or other digital content. Currently, there are four different types of Augmented Reality devices:
- Head-up displays – used in modern cars
- Holographic displays – for example from Samsung
- Smart glasses – Google Glass
- Handheld AR – modern smartphone and tablet cameras
But existing smart glasses and holographic displays are still expensive and therefore also not available to a lot of people. According to different sources, it will take at least 5 to 10 more years until AR technology is mature enough and available for everybody. Augmented Reality is currently mainly used for games like Pokémon GO or image filters on Snapchat and Instagram but this technology has a lot more potential for all industries.

Augmented Virtuality (AV)
Augmented Virtuality (AV) is one of the lesser-known immersive technologies. It is also a Mixed Reality technology and is situated between AR and VR on the Reality – Virtuality Continuum. Most of the time, AV applications and devices are just described as Mixed Reality. The term Augmented Virtuality is almost exclusively used in scientific papers. Examples for AV include computer games with real players, virtual concerts with real artists and real people on virtual backgrounds in video conference calls.
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual Reality is generally achieved with a head-mounted display and describes a fully immersive experience in a completely virtual world with no real objects. VR systems are using hardware, software, sensors and displays to create a computer-generated environment and allow the user to move in this world. With the help of controllers, it is also possible to move objects, arms or guns. Virtual Reality is currently mainly used for playing games but it also has a lot of potential for the health sector, the military, engineers and other industries.
„Virtual Reality refers to immersive, interactive, multi-sensory, viewer-centered, three-dimensional computer-generated environments and the combination of technologies required to build these environments.“
(Carolina Cruz-Neira, SIGGRAPH ’93 Course Notes „Virtual Reality Overview“)
This video shows a perfect example of a VR Game (Beat Saber) in an AV Video. The player is just able to see the boxes, scores and lightsabers during the playing experience but we can see an AV Video with the player in front of the virtual world.
Resources
Books
Virtual und Augmented Reality (VR/AR), Grundlagen und Methoden der Virtuellen und Augmentierten Realität from Ralf Dörner, Wolfgang Broll, Paul Grimm, Bernhard Jung, 2019
Medieninnovationen AR und VR, Erfolgsfaktoren für die Entwicklung von Experiences from Elle Langer, 2020
Web
https://www.futurelearn.com/info/courses/introduction-to-virtual-reality/0/steps/98720
https://www.ionos.at/digitalguide/online-marketing/verkaufen-im-internet/extended-reality/
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/231514051_A_Taxonomy_of_Mixed_Reality_Visual_Displays
https://www.softwebsolutions.com/resources/best-practices-for-extended-reality.html
https://www.infopulse.com/blog/how-does-augmented-reality-affect-the-automotive-industry-today/
https://charliefink.medium.com/vr-ar-mr-defined-finally-ef255ba1002d
https://news.microsoft.com/de-de/microsoft-erklaert-was-ist-mixed-reality-definition-funktionen/
https://uxdesign.cc/augmented-reality-device-types-a7668b15bf7a
https://augray.com/blog/extended-reality-is-transforming-the-way-cars-are-bought-heres-how/
