While Artificial Intelligence is getting used more now than ever before, the concept is not new. John McCarthy was already talking about “the science and engineering of making intelligent machines” back in the 1950s. Because of his numerous contributions to the field of Computer Science and AI he was also called the father of AI. Artificial Intelligence is a sub-field of Computer Science and is about how machines imitate human intelligence. It is rather about being human-like than becoming human. AI is also commonly described as any task performed by a machine that would have previously been done by a human, but there are a lot of different definitions. These definitions are shifting based on the goal the AI system has to achieve.
“The theory and development of computer systems able to perform tasks normally requiring human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and translation between languages.”
– Oxford Dictionary
“artificial intelligence (AI), the ability of a digital computer or computer-controlled robot to perform tasks commonly associated with intelligent beings.”
– The Encyclopedia Britannica
Types of AI
Artificial Intelligence can be divided into different types. These types can either be based on the abilities/capabilities or on the level of intelligence/functionalities of the system.
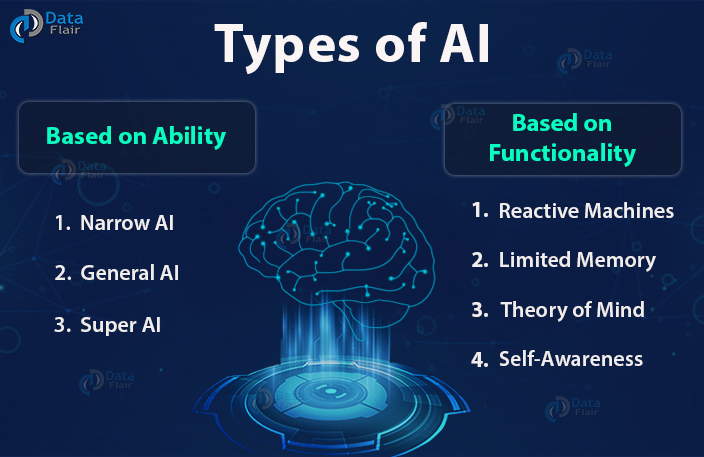
Based on Capability
Narrow AI
Narrow AI is also known as Weak AI or Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) and is focused on one single “narrow” task. This type is not able to do anything that was not programmed and targets only a single subset of cognitive abilities.
The Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) is the most common type of AI at the moment. It also includes more complex systems which are able to teach themselves with Machine Learning or Deep Learning. Most people nowadays are already using this type of AI on a daily basis. It is used in all personal assistants like Siri and Alexa, chatbots on websites, translating software, the Google page ranking system and many more. Narrow AI is also used in the health sector and is able to diagnose cancer and other illnesses with a very high accuracy by analyzing images from MRI’s.
General AI
General AI is also known as Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and these systems will have the same capabilities as humans. They can learn, perceive and understand like a human being. But because there is currently not enough knowledge about the functionality of the human brain to develop these systems, they are still under development and will not be available anytime soon.
The best attempts on Artificial General Intelligence also include simulations on the fastest supercomputers. Back in 2011 the Fujitsu K computer was able to simulate one single second of neural activity in about 40 minutes. The successor of this supercomputer, the Fugaku, is the fastest supercomputer at the moment and has a processing power of about 415 petaFlops. But the US government is already building an even faster supercomputer named Frontier. Frontier will have a processing power of about 1.5 exaFlops and will go online later this year. This supercomputer will also be the first machine with more processing power than the human mind (about 1 exaFlop).
Super AI
Super AI is also called Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) and will be more capable than any human. This technology is currently far away from becoming real but it would be the most capable form of intelligence on earth. Artificial Super Intelligence would also be able to perform incredibly well in creative tasks like design, decision making and even in emotional relationships. These systems will be better than any human at everything they do and may even take over the world.
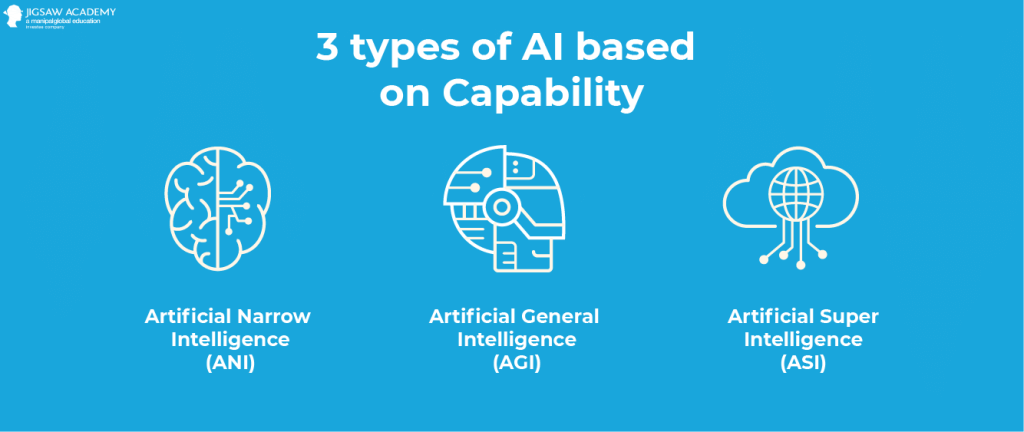
Based on Functionality
Reactive Machines
Reactive Machines are the oldest form of Artificial Intelligence and therefore also have extremely limited functionalities. These systems do not have a memory and are not able to learn from previously gained experiences. Reactive Machines are only using present data for solving specific tasks.
One of the most popular examples would be IBM’s Deep Blue. This machine defeated chess grandmaster Garry Kasparov in 1997. Deep Blue is able to identify the pieces on a chessboard, knows how each of them is moving and makes predictions about the next moves. But it ignores everything that happened before the present moment. It is looking at the chessboard after every move and starts deciding from there.
Limited Memory
Limited Memory is the most common type of functionality based AI’s. It is able to learn from data and base the decisions on this data. This type of Artificial Intelligence is using data from big databases as a training for future problems. Limited Memory is currently used for voice assistants, image recognition, chatbots, cars with autonomous driving capabilities and self-driving cars.
Theory of Mind
Theory of Mind will be the next level of AI systems. This type of Artificial Intelligence will be able to understand needs, emotions, beliefs and thought processes and will therefore be especially useful for researchers. Theory of Mind will be successful when systems are able to truly understand human needs.
Self Awareness
Self Awareness will be the final stage of Artificial Intelligence and is currently just existing hypothetically. Systems of this type will also have emotions, needs, beliefs and even desires of its own. Despite this technology being decades away from becoming real, people are already thinking about these systems and if they will take over humanity and enslave all humans.
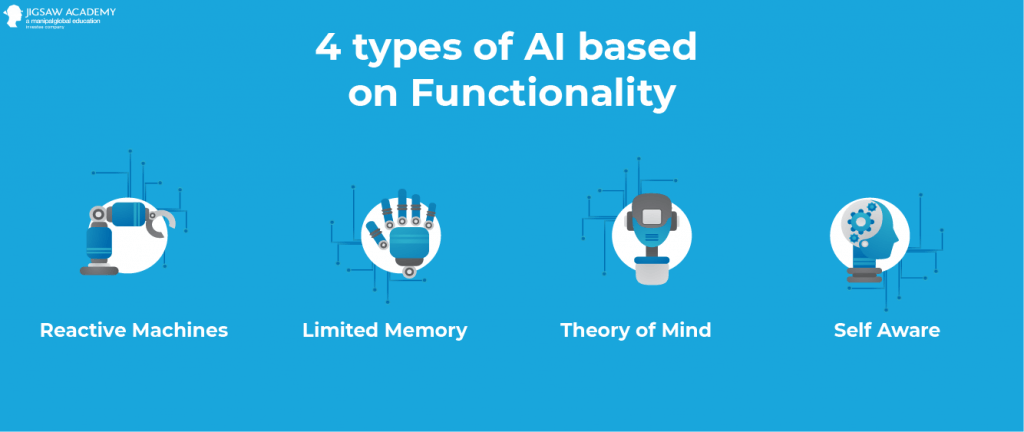
Subsets of AI
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is one of the most popular and also most important subsets of AI. It helps AI systems to learn and improve their capabilities without being programmed. Systems are becoming better and better at specific tasks because of it.
We are already using systems with ML in our daily lives. The most popular technologies powered by Machine Learning include personal assistants, targeted advertisements on social media, image recognition software and traffic predictions on services like Google Maps.
ML uses Neural Networks and other algorithms and can be divided into the following categories: Supervised Learning, Unsupervised Learning and Reinforcement Learning.
Neural Networks
Neural Networks are a subset of Machine Learning. They are modeling themselves by creating an artificial network with an algorithm based on the human brain. Neural Networks are trained by databases with a large set of labeled data. The most common databases consist of images and the correlating labels.
If you feed a Neural Network with pictures of thousands of traffic signs and their label, it is able to inspect and analyze these pictures, learn a formula based on the data, divide it into different layers and finally put the signs into different categories. A Neural Network that was trained like this is able to recognize every common traffic sign next to the road, categorize it and show the driver the current speed limit for example.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a Machine Learning technique and teaches machines how to learn. It is also called Deep Neural Learning and is a subset of Neural Networks.
Deep Learning is also used in the automotive industry. Systems like driverless cars or voice assistants use it to analyze thousands of hours of videos and images. Self-driving cars can learn how to drive and navigate on specific roads by studying road patterns, driving habits of existing humans and other vehicles on the road. But this process also requires a lot of data to work properly.
Artificial Intelligence is already used across nearly all industries. AI is completing our words as we type them, vacuuming our floors in every corner of the room, providing directions while avoiding high traffic roads, matching up passengers for ridesharing services and recommending what we should buy next on Amazon or watch next on Netflix.
Resources | part 1
https://www.britannica.com/technology/artificial-intelligence
https://interestingengineering.com/the-three-types-of-artificial-intelligence-understanding-ai
https://www.edureka.co/blog/types-of-artificial-intelligence/
https://www.ibm.com/cloud/learn/what-is-artificial-intelligence
https://builtin.com/artificial-intelligence
https://learn.g2.com/applications-of-artificial-intelligence
https://www2.deloitte.com/fi/fi/pages/technology/articles/part1-artificial-intelligence-defined.html
